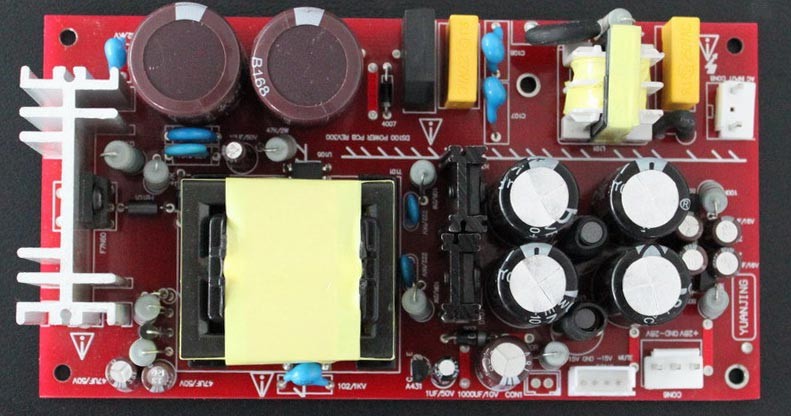
Power electronics is the application of solid-state electronics to the control and conversion of electric power.
The first high power electronic devices were mercury-arc valves. In modern systems the conversion is performed with semiconductorswitching devices such as diodes, thyristors and transistors, pioneered by R. D. Middlebrook and others beginning in the 1950s. In contrast to electronic systems concerned with transmission and processing of signals and data, in power electronics substantial amounts of electrical energy are processed. An AC/DC converter (rectifier) is the most typical power electronics device found in many consumer electronic devices, e.g. television sets, personal computers, battery chargers, etc. The power range is typically from tens of watts to several hundred watts. In industry a common application is the variable speed drive (VSD) that is used to control an induction motor. The power range of VSDs start from a few hundred watts and end at tens of megawatts.
The power conversion systems can be classified according to the type of the input and output power
- AC to DC (rectifier)
- DC to AC (inverter)
- DC to DC (DC-to-DC converter)
- AC to AC (AC-to-AC converter)
- سه شنبه ۳۱ مرداد ۹۶ ۱۳:۲۰ ۲۰۲ بازديد
- ۲۶ ۱۵
- ادامه مطلب
- ۰ نظر